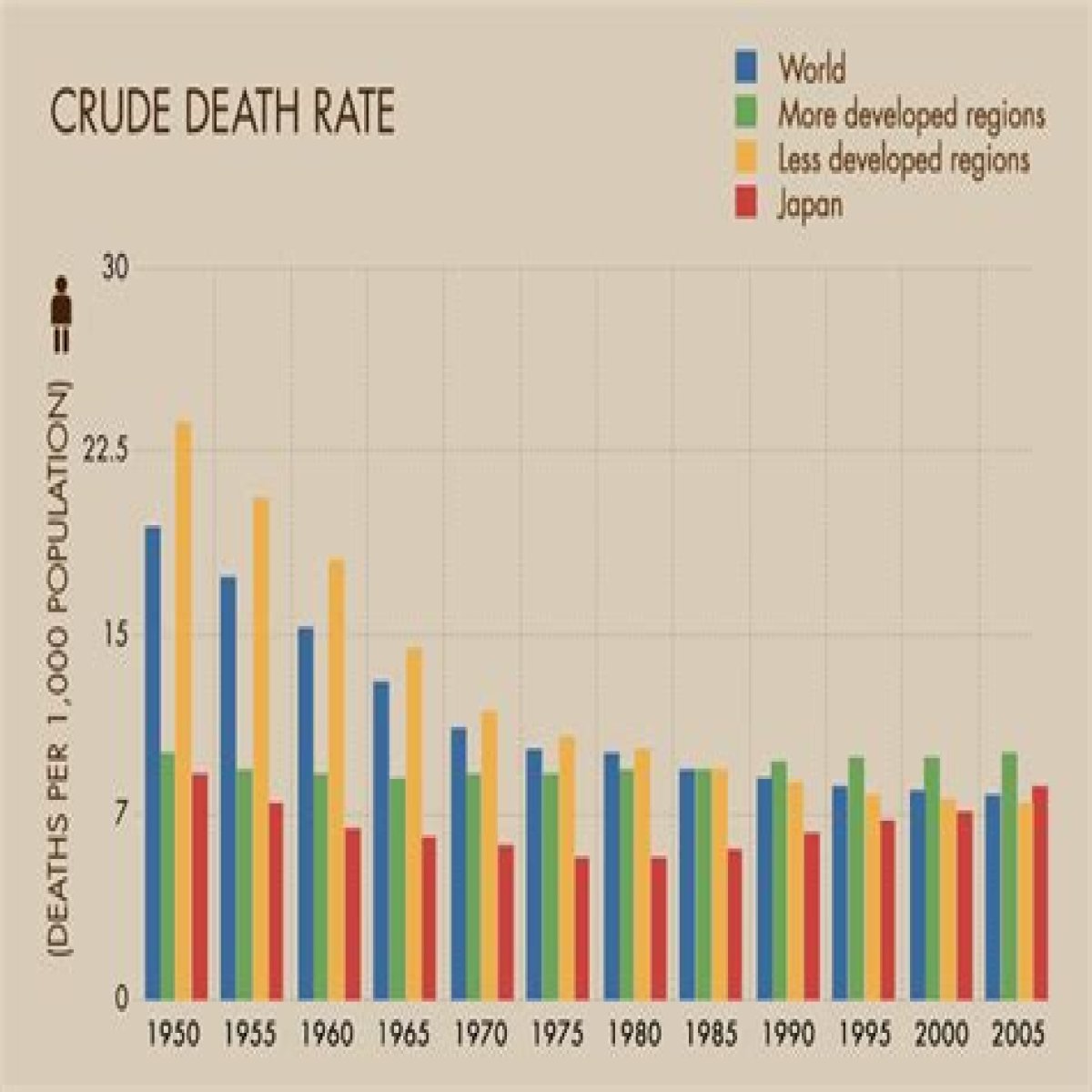
What is the crude death rate?
The crude death rate is a measure of the overall mortality in a population, calculated by dividing the number of deaths in a given year by the total population in that year and multiplying the result by 1,000. It is expressed as the number of deaths per 1,000 population.
The crude death rate is a useful indicator of the overall health and well-being of a population. It can be used to track changes in mortality over time, compare mortality rates between different populations, and identify populations with high mortality rates that may need additional public health interventions.
The crude death rate is a relatively simple measure to calculate, but it can be affected by a number of factors, including the age distribution of the population, the leading causes of death, and the availability of healthcare. As a result, it is important to consider these factors when interpreting crude death rates.
Despite its limitations, the crude death rate remains a valuable tool for public health surveillance and can provide important insights into the health of a population.
- Crude Death Rate
- Indicator of overall health and well-being
- Used to track changes in mortality over time
- Can identify populations with high mortality rates
- Relatively simple to calculate
- Can be affected by age distribution, leading causes of death, and healthcare availability
- Valuable tool for public health surveillance
- Provides insights into the health of a population
- FAQs on Crude Death Rate
- Conclusion
Crude Death Rate
The crude death rate is a measure of the overall mortality in a population, calculated by dividing the number of deaths in a given year by the total population in that year and multiplying the result by 1,000. It is expressed as the number of deaths per 1,000 population.
- Indicator of overall health and well-being
- Used to track changes in mortality over time
- Can identify populations with high mortality rates
- Relatively simple to calculate
- Can be affected by age distribution, leading causes of death, and healthcare availability
- Valuable tool for public health surveillance
- Provides insights into the health of a population
The crude death rate is a useful indicator of the overall health and well-being of a population. It can be used to track changes in mortality over time, compare mortality rates between different populations, and identify populations with high mortality rates that may need additional public health interventions.
Despite its limitations, the crude death rate remains a valuable tool for public health surveillance and can provide important insights into the health of a population.
Indicator of overall health and well-being
The crude death rate is a valuable indicator of the overall health and well-being of a population. It provides a snapshot of the mortality experience of a population, and can be used to track changes in mortality over time, compare mortality rates between different populations, and identify populations with high mortality rates that may need additional public health interventions.
The crude death rate is influenced by a number of factors, including the age distribution of the population, the leading causes of death, and the availability of healthcare. For example, populations with a high proportion of older adults will typically have higher crude death rates than populations with a younger age distribution. Similarly, populations with a high prevalence of chronic diseases, such as heart disease or cancer, will typically have higher crude death rates than populations with a lower prevalence of these diseases. The availability of healthcare can also affect the crude death rate. Populations with access to high-quality healthcare will typically have lower crude death rates than populations with limited access to healthcare.
The crude death rate is a useful tool for public health surveillance and can provide important insights into the health of a population. However, it is important to consider the limitations of the crude death rate when interpreting the results. The crude death rate does not provide information on the causes of death, and it can be affected by changes in the age distribution of the population. As a result, it is important to use the crude death rate in conjunction with other measures of mortality, such as the age-adjusted death rate or the infant mortality rate, to get a more complete picture of the mortality experience of a population.
Used to track changes in mortality over time
The crude death rate is a valuable tool for tracking changes in mortality over time. By comparing the crude death rates of a population over a period of years, it is possible to see how the overall mortality experience of the population is changing. This information can be used to identify trends in mortality, such as whether the overall mortality rate is increasing or decreasing, and to assess the effectiveness of public health interventions aimed at reducing mortality.
For example, the crude death rate in the United States has been declining for many years. This decline is due to a number of factors, including improved healthcare, better nutrition, and safer working conditions. The decline in the crude death rate has led to a longer life expectancy for Americans.
Tracking changes in mortality over time is an important part of public health surveillance. By monitoring the crude death rate and other measures of mortality, public health officials can identify trends in mortality and assess the effectiveness of public health interventions. This information can be used to develop and implement policies and programs aimed at reducing mortality and improving the overall health of the population.
Can identify populations with high mortality rates
The crude death rate can be used to identify populations with high mortality rates. This information can be used to target public health interventions and improve the overall health of the population.
- Geographic areas
The crude death rate can be used to identify geographic areas with high mortality rates. This information can be used to target public health interventions to these areas and improve the health of the population.
- Socioeconomic groups
The crude death rate can be used to identify socioeconomic groups with high mortality rates. This information can be used to develop and implement policies and programs aimed at reducing mortality in these groups.
- Age groups
The crude death rate can be used to identify age groups with high mortality rates. This information can be used to develop and implement public health interventions tailored to the specific needs of these age groups.
- Racial and ethnic groups
The crude death rate can be used to identify racial and ethnic groups with high mortality rates. This information can be used to develop and implement public health interventions tailored to the specific needs of these groups.
Identifying populations with high mortality rates is an important step in reducing mortality and improving the overall health of the population. The crude death rate is a valuable tool that can be used to identify these populations and target public health interventions.
Relatively simple to calculate
The crude death rate is a relatively simple measure to calculate, which makes it a valuable tool for public health surveillance. The formula for calculating the crude death rate is:
Crude death rate = (Number of deaths in a given year / Total population in that year) x 1,000
This formula can be used to calculate the crude death rate for a specific geographic area, such as a city, county, or state, or for a specific population group, such as a racial or ethnic group or an age group.
- Data availability
The data needed to calculate the crude death rate is typically available from government agencies, such as the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) in the United States. This data is often collected through vital records systems, which track births, deaths, and other vital events.
- Straightforward calculation
Once the data is available, the crude death rate can be calculated using a simple formula. This makes it a relatively easy measure to calculate, even for non-statisticians.
- Comparable across populations
The crude death rate can be used to compare mortality rates between different populations, such as different countries or different racial or ethnic groups. This makes it a useful tool for identifying populations with high mortality rates that may need additional public health interventions.
Overall, the crude death rate is a relatively simple measure to calculate, which makes it a valuable tool for public health surveillance and for comparing mortality rates between different populations.
Can be affected by age distribution, leading causes of death, and healthcare availability
The crude death rate can be affected by a number of factors, including the age distribution of the population, the leading causes of death, and the availability of healthcare.
Age distribution
The age distribution of a population can have a significant impact on the crude death rate. Populations with a high proportion of older adults will typically have higher crude death rates than populations with a younger age distribution. This is because older adults are more likely to die from chronic diseases, such as heart disease and cancer.
Leading causes of death
The leading causes of death in a population can also affect the crude death rate. Populations with a high prevalence of chronic diseases, such as heart disease or cancer, will typically have higher crude death rates than populations with a lower prevalence of these diseases.
Availability of healthcare
The availability of healthcare can also affect the crude death rate. Populations with access to high-quality healthcare will typically have lower crude death rates than populations with limited access to healthcare. This is because access to healthcare can help to prevent and treat diseases, and can also improve the quality of life for people with chronic diseases.
It is important to consider these factors when interpreting the crude death rate. The crude death rate does not provide information on the causes of death, and it can be affected by changes in the age distribution of the population and the availability of healthcare. As a result, it is important to use the crude death rate in conjunction with other measures of mortality, such as the age-adjusted death rate or the infant mortality rate, to get a more complete picture of the mortality experience of a population.
Valuable tool for public health surveillance
The crude death rate is a valuable tool for public health surveillance because it provides a snapshot of the overall mortality experience of a population. It can be used to track changes in mortality over time, compare mortality rates between different populations, and identify populations with high mortality rates that may need additional public health interventions.
For example, the crude death rate has been used to track the progress of the COVID-19 pandemic. By comparing the crude death rates in different countries over time, public health officials have been able to identify countries that have been hit hardest by the pandemic and target public health interventions to these countries.
The crude death rate is also a valuable tool for identifying populations that are at high risk of dying from specific diseases. For example, the crude death rate for cancer is higher among older adults than among younger adults. This information can be used to develop and implement public health interventions aimed at reducing cancer mortality among older adults.
Overall, the crude death rate is a valuable tool for public health surveillance. It can be used to track changes in mortality over time, compare mortality rates between different populations, and identify populations that are at high risk of dying from specific diseases.
Provides insights into the health of a population
The crude death rate provides insights into the health of a population by reflecting the overall mortality experience. It can be used to track changes in mortality over time, compare mortality rates between different populations, and identify populations with high mortality rates that may need additional public health interventions.
- Overall mortality
The crude death rate provides a measure of the overall mortality experience of a population. It can be used to track changes in mortality over time and compare mortality rates between different populations. This information can be used to identify trends in mortality and assess the effectiveness of public health interventions aimed at reducing mortality.
- Causes of death
The crude death rate can also provide insights into the leading causes of death in a population. By examining the causes of death in a population, public health officials can identify the most common causes of death and develop targeted interventions to reduce mortality from these causes.
- Risk factors
The crude death rate can also be used to identify risk factors for mortality. By examining the characteristics of populations with high mortality rates, public health officials can identify the risk factors that are most strongly associated with mortality. This information can be used to develop targeted interventions to reduce mortality from these risk factors.
- Vulnerable populations
The crude death rate can also be used to identify vulnerable populations. By examining the mortality rates of different population groups, public health officials can identify the populations that are most vulnerable to death. This information can be used to develop targeted interventions to reduce mortality in these populations.
Overall, the crude death rate provides valuable insights into the health of a population. It can be used to track changes in mortality over time, compare mortality rates between different populations, identify the leading causes of death, and identify risk factors for mortality. This information can be used to develop targeted interventions to reduce mortality and improve the health of the population.
FAQs on Crude Death Rate
The crude death rate (CDR) is a measure of the overall mortality in a population. It is calculated by dividing the number of deaths in a given year by the total population in that year and multiplying the result by 1,000. It is expressed as the number of deaths per 1,000 population.
Here are some frequently asked questions about the CDR:
Question 1: What does the CDR measure?
The CDR measures the overall mortality in a population. It provides a snapshot of the mortality experience of a population at a given point in time.
Question 2: How is the CDR calculated?
The CDR is calculated by dividing the number of deaths in a given year by the total population in that year and multiplying the result by 1,000.
Question 3: What are the limitations of the CDR?
The CDR does not provide information on the causes of death or the age distribution of the population. It is also important to note that the CDR can be affected by changes in the population size and age distribution over time.
Question 4: How is the CDR used?
The CDR is used to track changes in mortality over time, compare mortality rates between different populations, and identify populations with high mortality rates that may need additional public health interventions.
Question 5: What are some factors that can affect the CDR?
The CDR can be affected by a number of factors, including the age distribution of the population, the leading causes of death, and the availability of healthcare.
Question 6: How can the CDR be used to improve public health?
The CDR can be used to identify populations with high mortality rates and target public health interventions to these populations. It can also be used to track the progress of public health interventions and assess their effectiveness.
The CDR is a valuable tool for public health surveillance and can provide important insights into the health of a population.
Next: Key Takeaways
Conclusion
The crude death rate (CDR) is a valuable tool for public health surveillance and can provide important insights into the health of a population. It is a relatively simple measure to calculate and can be used to track changes in mortality over time, compare mortality rates between different populations, and identify populations with high mortality rates that may need additional public health interventions.
The CDR is not without its limitations, but it remains a useful tool for public health professionals and policymakers. By understanding the CDR and its limitations, public health professionals can use it to improve the health of the population.
Unveiling The Mystery: Is Bunty Short For Penelope?The Ultimate Guide To Maven M2 Folder: Storage, Configuration, And Best PracticesUncover The Secrets: Resolving Imported Date Column Hierarchy Challenges In Power BI